Back to Glossary Home | Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
What is Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)?
Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) is a cloud computing model that provides enterprise IT organizations with on-demand access to computing resources (e.g. networking, data storage, processing, and virtualization) over the Internet.
How Does Infrastructure as a Service Work?
The IaaS Model Supports Multiple Cloud Platforms
The IaaS model can be utilized with all kinds of cloud platforms: public, private, and hybrid.
Large IaaS providers like AWS, Google, and Microsoft enable their customers to run application workloads in a multi-tenant public cloud environment, or within a logically isolated virtual private cloud (VPC) on public cloud infrastructure.
Another way for companies to leverage the IaaS model is by establishing a managed private cloud in a remote data center on infrastructure owned and managed by a third-party MSP. A third option is colocation services, where IT infrastructure owned by the enterprise is hosted in a third-party data center.
IaaS Providers Maintain IT Infrastructure
IaaS providers operate and maintain large data centers that house the physical infrastructure needed to support IaaS capabilities, including servers, networking equipment, data storage systems, and cloud compute resources like central processing units (CPUs) and graphical processing units (GPUs).
IaaS Services are Delivered Over the Internet
IaaS providers provide a web-based interface and APIs that allow their enterprise IT customers to request access to IT infrastructure within the data center on an as-needed basis. Once the infrastructure has been provisioned, customers can remotely configure cloud computing instances, utilize data storage capacity, or program virtual machines to support a variety of operational and business use cases.
IaaS Resources are Decoupled
A great advantage of IaaS cloud computing is that it decouples storage and compute resources. IaaS customers can provision compute resources and data storage independently of each other, scaling up processing capacity when necessary without having to pay for unneeded data storage, or scaling data storage capacity without incurring costs for excess compute. This type of resource decoupling makes IaaS more cost-efficient and less wasteful than deploying applications on-prem.
IaaS Services are Pay-as-You-Go
IaaS is an on-demand service with pay-as-you-go pricing. IaaS customers are given full flexibility to provision only the resources they need for a specific use case and only pay for exactly what they use. Many IaaS providers offer a “free tier” of service, allowing users to operate a cloud instance for a limited time or access a limited amount of data storage capacity for no charge. Beyond that, IaaS providers typically charge by the minute for cloud computing instances and by the gigabyte (GB) for data storage and transfer.
Why is Infrastructure as a Service Important?
Before the IaaS cloud computing model was popularized in the mid-2000s, there was a much higher barrier to entry for IT organizations to access and scale IT infrastructure.
An organization that needed additional computing capacity, data storage, or virtualization capabilities had no choice but to purchase the required hardware, set up a data center to house it, and establish a team of data center technicians and engineers to maintain it.
The high capital equipment and facility costs, substantial management overhead, and expensive salaries required to establish and operate these data centers made it cost-prohibitive for all but the best-funded enterprises to access the IT infrastructure they might need to digitize their operations, power innovation, and accelerate business growth.
The IaaS cloud computing model replaces high equipment, facility, and operational costs with a simple web-based interface for provisioning IT infrastructure and an affordable pay-as-you-go pricing model, enabling IT organizations to access the computing resources, data storage capacity, and virtualization capabilities they need without having to build and maintain their own data centers.
IaaS computing has made it substantially more affordable for millions of their customers to access the IT infrastructure they need to power critical business use cases that range from big data analytics to software testing/development and disaster recovery.
3 Types of Infrastructure as a Service Resources
1. Compute
IaaS providers offer cloud-based virtual machines called “instances” that allow their customers to run application workloads in the cloud. A cloud instance is like a virtual computer with its own memory and processing power that IaaS customers can configure to analyze data, run an application, or for a variety of other use cases.
2. Storage
IaaS providers offer cloud-based data storage systems that allow their customers to cost-effectively store vast amounts of data in the cloud. Block and file storage systems are sometimes offered, but the most common type of cloud storage system is object storage. Cloud object storage systems are cost-effective, highly durable, and can scale to meet the data storage demands of growing organizations.
3. Networking
IaaS providers operate and maintain the infrastructure that enables secure communication, traffic routing, and data transfer between cloud-based applications and services. This includes virtual networks and subnets, network connections between on-prem and cloud environments, virtual private clouds and VPNs, load balancers, and Content Delivery Networks (CDNs).
These networking resources provide the capabilities that enterprise organizations need to control the flow of data between cloud-based applications and ensure efficient communication between infrastructure components that work together to support business use cases.
6 Advantages of Infrastructure as a Service
Reduces CAPEX and Enhances Cost Efficiency
IaaS allows enterprise organizations to flexibly scale their cloud infrastructure without incurring the capital costs of purchasing hardware or setting up a data center. Pay-as-you-go pricing enhances IT cost efficiency by ensuring that IaaS customers only pay for what they use.
Enables Global Remote Management of IT Infrastructure
Before IaaS, IT and DevOps teams had to manage their IT infrastructure from inside the physical data center. With access to infrastructure as a service, IT organizations can now provision, manage, and utilize IT infrastructure from anywhere in the world with an Internet connection.
Increases IT Infrastructure Scalability and Reduces Waste
For organizations with on-prem data centers, scaling IT infrastructure to meet high demand for a service means incurring both up-front capital costs and ongoing maintenance costs for the new hardware. If the high demand is temporary, the new equipment may be underutilized, resulting in wasted time and money.
A great advantage of cloud-based IT infrastructure is that it’s highly scalable, allowing customers to flexibly provision resources, scale compute or storage capacity based on demand, and only pay for what is used.
Increases Availability and Reliability of Critical Applications and Services
IaaS providers offer high levels of reliability and service availability, ensuring that their customers can rapidly and predictably access the resources they need to support critical business applications and workloads.
Improves Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery
IaaS providers typically operate multiple data centers and can replicate compute instances or data across multiple isolated hardware nodes or availability zones to enable rapid failover and ensure business continuity in case of an unplanned disaster or service interruption.
Improves Innovation and Speed to Market
Eliminating the complexity, management overhead, and high costs that would normally be associated with managing IT infrastructure allows IaaS customers to focus less on infrastructure management and more on innovating, creating business value, and getting new products to market.
7 IaaS Use Cases You Should Know
Check out these 7 public cloud use cases that leverage the IaaS cloud computing model.
Lift and Shift Migration
IT organizations that operate legacy applications in on-premise data centers can reduce management complexity and operating costs by migrating those applications into the cloud and running application workloads on cloud-based infrastructure.
Software Testing and Development
IaaS service providers make it easy for enterprise DevOps teams to spin up new cloud instances or virtual environments to support software testing and development cycles.
Handling Traffic Spikes
Infrastructure-as-a-Service is the most cost-effective way for IT organizations to handle large traffic spikes or periods of increased demand for an application or service. IaaS service providers make it easy to elastically scale the availability of compute or storage resources based on demand.
Big Data Analytics
Storing and analyzing data at scale requires a large data storage capacity and a lot of processing power. IaaS service providers allow IT organizations to access these critical resources on an on-demand basis, decreasing the barrier to entry for analyzing big data and extracting valuable insights.
Enabling Data Access
IaaS service providers deliver the most cost-effective data storage thanks to economies of scale from operating the world’s largest data centers. Organizations benefit from high durability storage, built-in security and access management tools, and the ability to access enterprise data from anywhere in the world.
Data Backup and Disaster Recovery
IT organizations can leverage cost-effective, scalable, and durable data storage in the cloud to regularly back up data from critical operational systems. This can help prevent data loss and enable faster disaster recovery in the event of an unplanned service outage.
High Performance Computing
High-performance computing (HPC) involves aggregating computer resources into custom-built supercomputers that can support the most demanding application workloads. IT organizations can leverage high-density colocation services with advanced power distribution and cooling systems from vendors like TierPoint to deploy HPC workloads.
Hosting Web-based Applications and Services
The IaaS cloud computing model allows IT organizations to build, test, deploy, and host software-based applications and services in the cloud without the added burden of managing the underlying infrastructure.
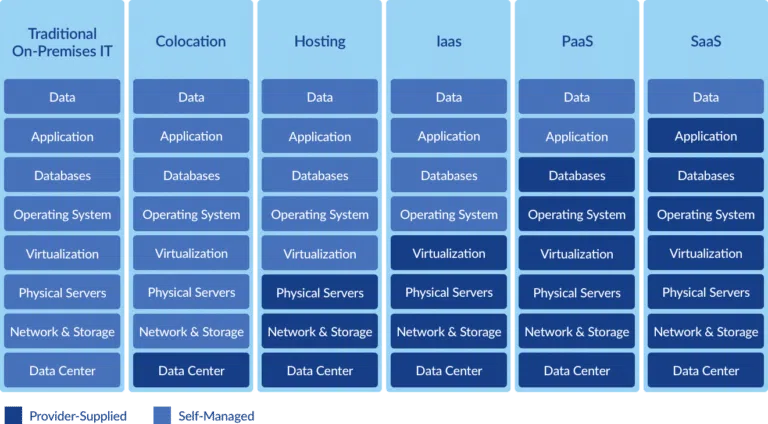
IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS: What is the Difference?
Wondering about the difference between IaaS vs. (PaaS) vs. (SaaS)?
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) is a software distribution model where developers host software products in the cloud. Instead of downloading these products to install and run them on local machines, customers consume SaaS products over the Internet, often in exchange for a monthly subscription fee. With SaaS, customers get all the benefits of the software without any management overhead.
Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) is a cloud computing model that’s designed to streamline the software development life cycle for DevOps teams. PaaS vendors provide a cloud-based software development platform that makes it easier for DevOps teams to build, run, and manage software applications without maintaining the underlying infrastructure. PaaS vendors manage the underlying hardware, along with operating systems, middleware, and runtime.
Start Leveraging IaaS with TierPoint Cloud Services and Solutions
TierPoint offers cloud services and solutions like managed hosting and high-density colocation, giving our customers on-demand access to powerful IT infrastructure and resources.
TierPoint manages, maintains, and secures our modern data centers and cutting-edge IT infrastructure, allowing our customers to host applications, back up data, handle traffic spikes, or implement failover processes without the added cost and complexity of managing IT resources.
Ready to learn more?
Book an intro call with us and discover how you can streamline business operations and accelerate innovation with IaaS from TierPoint.