February 20, 2025 | Channing Lovett
The Role of AI and ML in Cybersecurity: Benefits and Use Cases

As security threats continue to evolve and change, and as conversations continue around AI and security best practices, businesses need to be equipped with technologies that can respond to these risks. “You have to use AI at this point. let’s say attackers are using it, and they’re using it to create things. It’s a component of automation and how fast things are being thrown out these days.” says Richard Tallman, Senior Director of Global Cloud Security and MSP at Bitdefender, emphasizing the necessity of AI in modern cybersecurity. This includes incorporating artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies into cybersecurity strategies. By understanding the role that AI and ML tools play in cybersecurity, businesses can be better equipped to modernize their IT infrastructure with proactive technologies that move at the speed of evolving cyber threats.
Understanding AI and ML Technologies
Artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI/ML) and large language models (LLMs) are almost impossible to miss in daily life. These tools create systems that learn from users and change over time to better serve their intended purposes. While these AI/ML technologies offer a range of use cases, they can also place significant demands on infrastructure and come with new threats and ethical implications that businesses need to consider before embracing new technologies.
What Is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a field of computer science focused on creating systems that mimic human reasoning and reactions. This includes understanding language, recognizing patterns, solving problems, and making decisions. AI powers things like virtual assistants, self-driving cars, and fraud detection tools.
Generative AI (GenAI), an emerging type of artificial intelligence, takes the capabilities of traditional AI even further, creating new content based on what it has learned from existing data. As traditional AI primarily analyzes information, GenAI can write stories, generate realistic pictures, mimic human voices, and even help write computer code. It powers tools like chatbots, deepfake videos, and AI-generated artwork.
What Is Machine Learning (ML)?
Machine learning (ML) is a type of AI that powers the learning of a system without direct programming. Machine-learning algorithms can use patterns in data to predict future outcomes, make real-time decisions, or classify data in an available set. Training may be done with labeled data, unlabeled data, or through a reinforcement technique that rewards or punishes certain algorithmic decisions.
The Differences Between AI and ML
While closely related, AI and machine learning (ML) are not the same. AI encompasses a broad range of techniques, including rule-based systems and expert-designed solutions, to mimic human intelligence. ML, a subset of AI, relies on algorithms that learn from data to make predictions or decisions without explicit programming. This includes generative AI and agentic AI, but AI is not limited to ML-based approaches.
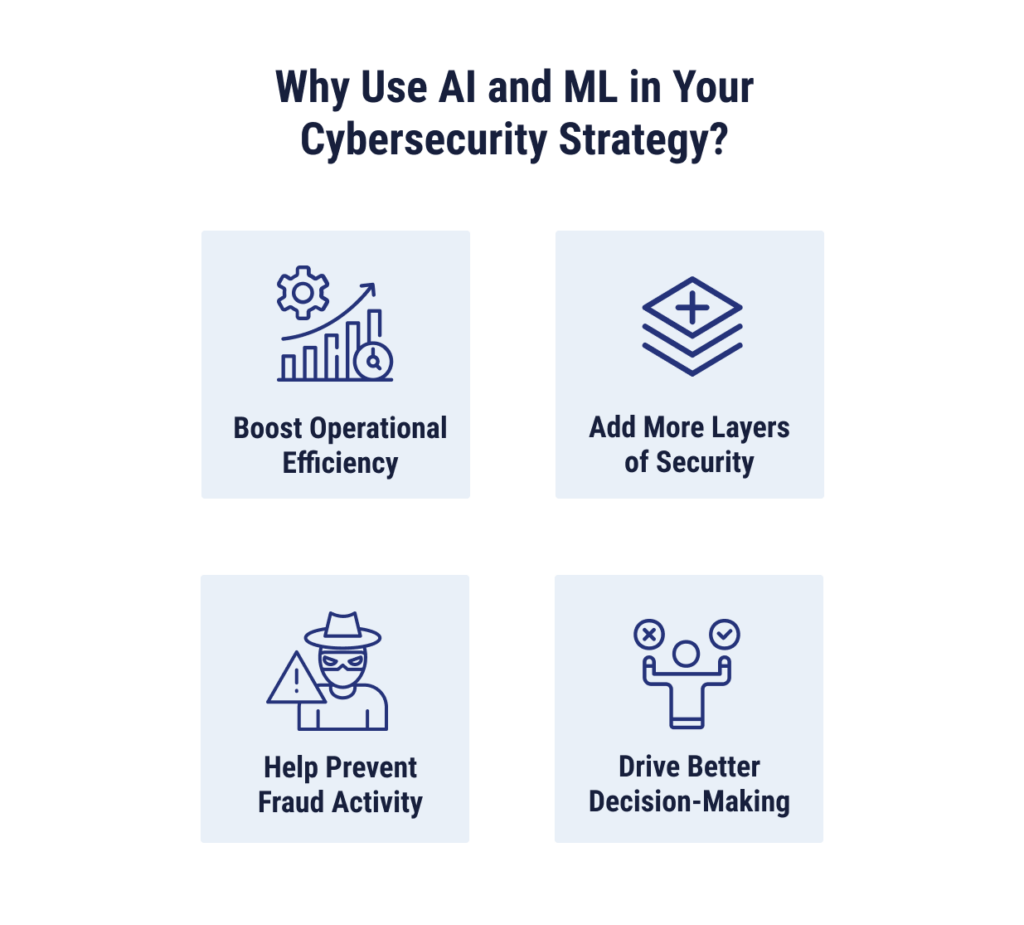
The Role of AI in Cybersecurity
AI is being used in powerful ways to improve the cybersecurity of businesses through the identification and mitigation of threats. It can even be used to train employees to spot potential malicious emails.
- Risk Assessment (or Informed Decision-Making): While human experts can be effective in spotting risks, this can be a time-consuming exercise and is limited to work hours and the amount of data a human is able to process in a certain amount of time. AI algorithms can use insights gathered from vast amounts of data to prioritize potential risks for further human intervention. This tool can make cybersecurity experts more effective because their efforts are more focused.
- Fraud Prevention: Similarly, AI systems can use expected patterns in datasets to identify anomalies that may be indicative of fraudulent activity. Spotting these issues in real time can reduce the damage done by fraudsters.
- Adaptive Security Measures: Cybercriminals will adapt to the security tools they’re trying to overcome, but AI can be one step ahead, developing adaptive security measures that adjust to changing threat landscapes. AI/ML tools can also detect zero-day exploits and other emerging threats before they may reach mainstream acknowledgement. Large language models and generative AI can also be used to generate realistic social engineering and phishing emails to train internal employees to spot potential threats.
- Operational Efficiency: By automating regular tasks, such as vulnerability scanning and incident response efforts, AI can free up time for security professionals to focus on tasks like developing new wide-ranging security strategies.
The Role of ML in Cybersecurity
Machine learning (ML) can enhance cybersecurity capabilities in threat detection, prediction, response, and aggregation.
- Threat Detection: Unusual patterns can spell malicious activity, something that ML algorithms can pick up on with unmatched efficiency. ML models can also effectively detect malware and potential phishing attempts, even as strategies shift over time.
- Predictive Analytics: Using historical data, ML can predict the likelihood of a future risk, as well as possible vulnerabilities before hackers are able to exploit them.
- Automated Response Systems: After a threat has been identified or predicted, ML models can also respond automatically.
- Data Aggregation: It’s hard to get a comprehensive view of the threat landscape without a tool that can aggregate everything. ML technologies can be used alongside security information and management (SIEM) tools to analyze and collect security events from distributed sources.
Potential Challenges with AI and ML in Cybersecurity
While AI and ML tools can positively influence an organization’s cybersecurity approach, they can also pose unexpected risks if they are not implemented and maintained properly.
- Data Privacy Concerns: Because AI/ML models need massive datasets to be trained, the process can pose concerns around how personal data is being collected and used to shape the tools. These technologies should be compliant with regulations like GDPR and CCPA when collecting data, and should also work to keep the data safe during training.
- False Positives and Negatives: False positives occur when an AI cybersecurity tool flags something legitimate as a threat. A false negative happens for the opposite reason, when actual threats are not detected. Both can pose problems by throwing focus away from real problems. AI models can also become biased based on the data sets on which they were trained, leading to unfair targeting of specific groups and individuals.
- Complexity and Cost of Implementation: It can be expensive to maintain, implement, and update AI/ML-based security solutions as technology evolves faster than these systems can be put in place. Doing this effectively can require specialized workers, dedicated budgets, and significant upfront investments.
- Keeping Up with Innovation in LLMs: As large language models (LLMs) evolve, so do the threats they pose. Attackers can use AI-generated content for phishing, deepfakes, and other cyber threats. Staying ahead means constantly adapting security strategies to keep up with these fast-moving advancements.
How Are Threat Actors Using AI Technologies?
Threat actors are using a variety of generative AI methods to make cyberattacks more sophisticated, efficient, and difficult to detect.
- Social Engineering and Phishing Attacks
- Highly convincing phishing emails: AI can generate grammatically correct, personalized, and context-aware phishing emails, making them more effective.
- Deepfake audio and video: Attackers use AI-generated voices and videos to impersonate executives (CEO fraud) or family members in scams.
- Automated chatbot scams: Malicious AI-driven chatbots can conduct phishing in real-time, responding intelligently to victims.
- Malware and Exploit Development
- Polymorphic malware: AI can help create malware that constantly changes its code to evade detection.
- Automated vulnerability exploitation: AI can rapidly analyze software for security flaws and generate exploit code.
- AI-assisted scripting: Threat actors use AI to refine and automate attack scripts.
- Misinformation and Disinformation Campaigns
- Fake news and propaganda: AI can generate realistic fake news articles or misinformation campaigns at scale.
- Synthetic media (deepfakes): AI-generated images, videos, and voices are used for political manipulation, stock market fraud, and reputation damage.
- AI-driven botnets: Social media manipulation using AI-powered bots to amplify misleading content.
- Fake news and propaganda: AI can generate realistic fake news articles or misinformation campaigns at scale.
- Synthetic media (deepfakes): AI-generated images, videos, and voices are used for political manipulation, stock market fraud, and reputation damage.
- AI-driven botnets: Social media manipulation using AI-powered bots to amplify misleading content.
- Credential Stuffing and Identity Theft
- Automated password cracking: AI can analyze leaked passwords and predict new ones more effectively.
- Synthetic identity fraud: AI can generate realistic fake identities (including profile pictures) for fraud.
- Bypassing CAPTCHA & MFA: AI models are used to defeat security mechanisms like CAPTCHAs and certain multi-factor authentication methods.
- Cyberattack Automation and Evasion
- AI-enhanced penetration testing: Threat actors use AI to conduct reconnaissance, identifying vulnerabilities faster.
- Automated attack orchestration: AI streamlines cyberattacks, reducing the need for human oversight.
- AI-powered evasion techniques: Attackers use AI to generate traffic patterns that avoid detection by security tools.
- Fraud and Financial Crimes
- Synthetic fraud: AI-generated fake IDs, credit card numbers, and transaction records are used for financial fraud.
- AI-enhanced investment scams: AI generates fake investment reports and impersonates financial experts.
- Voice phishing (vishing): AI-generated voices impersonate financial institutions or relatives to steal money.
- Data Poisoning and AI Model Manipulation
- Poisoning AI training data: Attackers manipulate datasets used to train security AI, degrading its accuracy.
- Adversarial AI attacks: Attackers craft data that AI models misinterpret, leading to incorrect outputs in security systems, autonomous vehicles, or facial recognition.
Best Practices for Implementing ML and AI Strategies
- Align initiatives with business goals.
Don’t chase the shiny object. Decide which projects will address the most critical business needs and develop solutions for them first. Maintaining an LLM-agnostic approach is a best practice, ensuring flexibility as innovation accelerates. The changes you’re looking to make should make sense within the scope of your business. - Invest in scalable infrastructure and tools.
AI/ML workloads can be demanding, and that demand is only going to increase over time. AI Cloud computing resources and infrastructure can help you scale alongside demand and implement the high-performance computing, networking, and storage necessary to support AI/ML workloads. However, when you take advantage of cloud-based AI, you also need to be mindful of cloud-specific security concerns. - Set your SOC team up for success.
Your security operations center (SOC) monitors and responds to security threats for your organization. AI/ML tools can automate the processes that make SOC teams more effective. SOC analysts should also understand how to use AI cybersecurity tools, as well as the threats that can come with AI/ML technologies. - Prioritize data quality and ethical practices.
When you are working on implementation, address ethical concerns associated with AI/ML, including fairness, transparency, accountability, and bias. Ensure the process is as open as possible and implement robust security measures to protect sensitive data that are used in AI/ML systems in your organization.
Make AI and ML Strategies Work for You
The best way for businesses to gain a competitive advantage on cybersecurity threats is by implementing artificial intelligence and machine learning strategies that can combat risks as they emerge. However, navigating the complexities of the AI/ML space alone can be challenging.
TierPoint offers IT advisory consulting services that assist businesses in choosing the right AI/ML strategies for their unique needs. Our strategic guidance can help you identify the right business applications for AI/ML technologies that will boost your security posture and help you stand out from others in your industry. Learn more about how you can build a more successful business with AI tools.

