April 2, 2024 | Channing Lovett
Ransomware Remediation: Effective Response & Prevention Guide

Ransomware is an ever-present problem in today’s business world, and is becoming more accessible for bad actors through ransomware as a service (RaaS). In March 2024, it was reported that a transaction involving 350 bitcoins (worth approximately $22 million USD) was sent to AlphV/BlackCat, a notorious hacker involved with RaaS. This transfer is suspected of being connected to a ransomware attack targeting the healthcare organization, Change Healthcare. The moments after a business experiences a ransomware attack are critical. Every decision made can result in substantial, long-ranging consequences, including increased ransoms, additional threats, and lasting damage to business revenue and reputation.
In these high-pressure scenarios, remediation should be the focus. We’ll discuss what ransomware remediation is, how it works, and the strategies organizations can implement to limit the impact of ransomware attacks.
What is Ransomware Remediation?
Ransomware remediation details the steps a business will take to recover from a ransomware attack. Even when businesses have plans to combat ransomware at its root, it can be difficult to avoid an attack. Hackers are constantly evolving their methods and approaches to find vulnerabilities in their victims’ systems. While it’s important to grow and change your cybersecurity methods over time, it’s equally important to be realistic and plan for the worst-case scenarios.
How Does it Work?
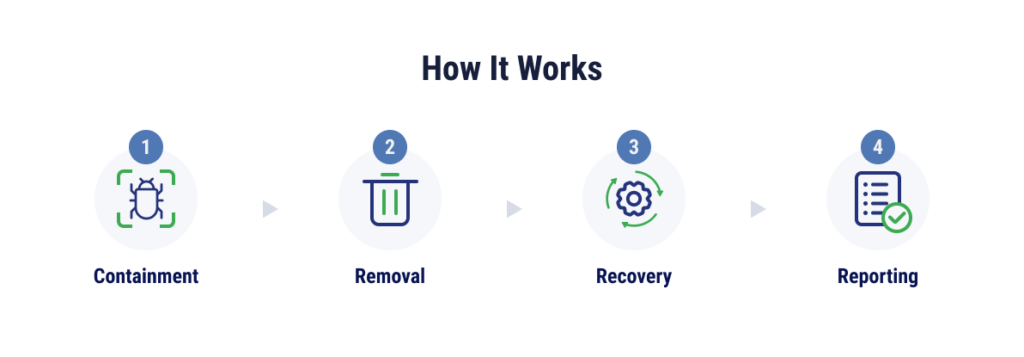
A ransomware remediation process starts with containing the ransomware, preventing it from spreading and encrypting additional files. From there, the ransomware should be removed. Then the recovery process begins, where files will be restored from secure backups. Finally, the attack may need to be reported to the authorities as well as all relevant parties, and the incident should be reviewed to identify and eliminate vulnerabilities that could cause future incidents.
Key Considerations for Effective Ransomware Remediation
Ransomware remediation can be most effective if you prioritize your recovery efforts, conduct an impact assessment, secure your evidence, communicate to necessary parties, and understand the full legal implications of ransomware attacks and your required response to them.

Prioritization for Recovery Efforts
Not every file or workload is mission-critical for your business. Your recovery efforts should be focused first on sensitive data and applications that are necessary to keep your core operations running. Prioritizing can speed up and simplify the recovery process.
Impact Assessment
Fixing the problems caused by ransomware attacks means that you need to start by assessing the damage. How many devices and systems have been affected by the ransomware? What data has been lost, either temporarily or permanently? And how severely are core operations impacted from the initial attack and its spread?
Secure Evidence
Businesses looking to mount a legal response to a ransomware attack will need to collect and document evidence along the way. Be sure to do this on a device that is not affected. It’s also a good idea to isolate the systems that have already been infected with ransomware to keep from tampering with evidence.
Communication Plans
Transparency and clear communication will help you build and secure trust with key stakeholders during the ransomware remediation process. Create a plan that can be executed as needed for communicating with employees, management, law enforcement, and important external relationships, including vendors, partners, and customers. Your remediation strategy should include a plan for who to share information with and when.
Legal Implications
Ransomware attacks can include legal ramifications. For example, you may be required to report the attack to authorities depending on your industry or the nature of your business. There may also be legal repercussions should you choose to pay the ransom.
Ransomware Remediation Strategies
After identifying the problem and alerting the proper organizational contacts to the ransomware attack, your business should engage in these 7 key strategies as part of a comprehensive ransomware remediation plan.
Containment and Isolation
Ransomware can spread quickly if not contained. Section off infected devices by disconnecting them from the network, or even taking the entire network offline in more severe cases. To aid in forensic investigations, capture system images and volatile memory contents of the infected devices. System images provide a complete snapshot of device storage, and volatile memory contents can hold forensic clues for what happened during the inciting incident.
Alert Law Enforcement and Cybersecurity Experts
Once you’ve contained and isolated problem devices, consult with security vendors and law enforcement authorities if required, who can provide further guidance and assistance with how to best approach remediation and potentially legal action.
Ransomware Identification and Eradication
After you feel like you’ve contained the problem, it’s time to identify and eradicate the cause, potentially with the help of outside experts. The type of ransomware infecting the system (such as scareware or lockerware) will also help you identify how to remove all traces of it from your systems. This might entail wiping your systems clean, rebuilding infected parts, resetting passwords, and addressing vulnerabilities in your current configurations.
Cybersecurity experts may have decryption tools your organization can use to restore your files. However, if decryption isn’t a possibility, you’ll want to restore data from backups to a clean environment.
Communication and Recovery
The recovery process takes time. Prioritize the systems that are most important to keeping your business functional, and communicate with employees, customers, and other key stakeholders so they know what to expect in the days and weeks to come.
Data Restoration and Backups
One of the best ways to defend your business against ransomware and other data breaches is by implementing a strong backup system that includes immutable and air-gapped backups. Now is the time to plan the failover to your recovery environment using your established recovery practices which should encompass your recovery point objectives (RPO) and recovery time objectives (RTO). Ensure that backups remain isolated to prevent them from being encrypted.
Post-Incident Review and Reporting
While you can’t protect against every potential threat, a post-incident review can help you summarize what you’ve learned from the recent ransomware attack and what you are changing in the future to prevent similar events from happening.
How to Prevent Future Ransomware Attacks After Remediation
After the ransomware remediation process, it’s important to consider what changes you can make to prevent the impact or likelihood of future attacks. Don’t forget to take these preventative measures after the urgency subsides.
Perform Routine Updates and Patching
Zero-day vulnerabilities serve as a common entry point for ransomware. Some businesses engage in routine updates and patching on “Patch Tuesday,” the second Tuesday of the month, when companies like Microsoft and Oracle commonly release patches for their software. Keeping a regular schedule, no matter what it is, is a great way to address known security shortcomings.
Leverage Tools and Software
Much of the work needed to prevent ransomware attacks can come from security software, such as antivirus, anti-malware, and endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools. The right tools can identify and block incoming threats before they get on your radar.
Conduct Employee Security Training
Employees are another common attack vector. Cybercriminals will use social engineering tactics, including highly targeted messages (spear phishing) to try to gain access to your systems. By regularly training employees on what to look for and how to spot potential threats, you can greatly reduce the risk of attacks from employee sources.
Apply User Permission Restrictions
Restrict user permissions in your systems to only include what’s necessary for them to perform their job functions. If an account gets compromised, this can reduce the potential damage to the rest of your organization. For special cases, you can always supply temporary additional access.
Complete Regular Vulnerability Assessments and Tests
In addition to regularly patching, conduct vulnerability assessments to fix problems before they can be exploited. With penetration testing, organizations can simulate the impact of an attack and find issues before the “real thing” happens.
Implement Continuous Monitoring and Analysis
Continuously monitoring detects patterns and anomalies in your environment, which can allow you to more quickly identify suspicious behavior that may be indicative of:
- A potential ransomware attack
- A malware infection
- Or other cybersecurity threat
One way you can do this is by adding security information and event management (SIEM) tools to your processes.
Review and Update Your Disaster Recovery Plan
Penetration testing is one way you can review your preparedness for ransomware and other disasters, but it should also be part of a larger disaster recovery plan. Review your lessons learned, update systems before the next incident or attack, and remember that maintaining your security posture is an ongoing engagement, not a one-off project, so testing should take place often.
Don’t Wait Until It’s Too Late to Prepare for Ransomware
The evolving threat landscape is likely to outpace your internal technologies and teams. Businesses need to work with strategic partners who can scale with the scope of new threats and secure trust from the inside out. TierPoint’s security and disaster recovery experts are here to help you stay ahead of the curve and meet new challenges proactively. Learn more about ransomware and our approach to emerging threats in our eBook.
Learn more about our Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS) and other solutions that can mitigate ransomware’s effects. Download our infographic to learn 13 steps to creating an effecitve disaster recovery plan.

FAQs
Ransomware is incredibly damaging and can be something businesses do not recover from if they don’t have solid backup and disaster recovery plans. Organizations can experience data loss, financial loss, downtime, and irreparable damage to their reputation.
Ransomware remediation generally involves containment, isolation, impact assessments, securing evidence, identifying and eradicating ransomware, decrypting and restoring files, communicating the recovery process, and conducting a post-incident review.
No matter how well you think your preventative measures are working, no business is 100% protected against ransomware attacks. Ransomware remediation is important to ensure your organization will be able to recover if you experience a ransomware attack.
