
Not all data your organization stores requires the same level of data protection, performance, and ease of access. Some of your data may be more archival, only accessed a few times per year, whereas other data may be accessed multiple times a day. Some data is more sensitive and confidential, such as financial data and patient information. Other data does not include personally identifiable information and will not require as much protection. Some businesses approach handling different types of data by allocating workloads to distinct cloud environments, using a multicloud strategy.
What is Multicloud Storage?
Multicloud storage is a strategy where businesses store their data across more than one cloud environment. This can be a combination of public and private clouds or several clouds of one type. For example, a business may store more sensitive data in a private cloud and less critical information with a public cloud provider, such as Microsoft Azure Blob Storage. Flexera’s 2024 State of the Cloud found that 89% of cloud decision-makers worldwide leverage multicloud environments. Multicloud environments are similar to hybrid cloud, which include a combination of cloud and on-premises environments.
How Does Multicloud Storage Work?
Storage in a multicloud environment operates based on how the organization wants to allocate and distribute its data. Common deciding factors can include cost, compliance, and performance needs. To integrate between cloud environments, specialized tools can be used, including application programming interfaces (APIs), to enable easier data management and access. Sometimes, businesses will create an abstraction layer to have a unified view of all cloud storage resources to make data management easier.
Multicloud Storage: Key Benefits and Challenges
Multicloud storage allows for greater scalability, flexibility, reliability, and cost-efficiency. However, connecting several cloud platforms can be daunting. Here are some of the benefits and challenges to consider.
Benefits of Multicloud Storage
Because you’re combining several cloud environments, you can choose the best storage services from each provider based on workload type. This allows you to optimize costs by selecting cost-effective options for each workload and scaling without exceeding requirements. Working with a single cloud provider can lead to vendor lock-in, but when businesses choose multicloud environments, they have more freedom to switch providers.
Challenges of Multicloud Storage
Freedom of choice also comes with difficulties in managing complexity. Different cloud platforms can have different pricing models, tools, and interfaces that need to be evaluated and reconciled, often with special technologies and tools. While integration can make managing workloads easier in the long term, the initial setup can be tricky. Transferring data between different clouds can also result in greater latency.
5 Key Technologies Used in Multicloud Storage
Data stored across multiple cloud service providers relies on tools and integrations to function effectively. Without these key technologies, businesses wouldn’t have strong data access, security, and management between platforms.
Application Programming Interfaces (APIs)
APIs enable applications to interact with data stored in various cloud environments by providing a standardized way to access, move, and manage data between cloud providers. For example, APIs can allow data analytics applications to access datasets that are stored in two different cloud storage tools.
Cloud Orchestration Tools
Automating tasks can make working in the cloud much easier. Cloud orchestration tools can automate tasks between cloud platforms that can otherwise be complex. Cloud orchestration tools include Azure Resource Manager, Terraform, AWS CloudFormation, and OpenStack. These tools can help define cloud infrastructure based on a ruleset and provision resources automatically across cloud providers such as AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
Containerization Technologies
Applications can also be packaged with their dependencies into containers, which serve as standardized units that can be deployed in a multicloud environment, no matter the underlying data center infrastructure. Technologies, such as Docker, can bundle code, libraries, and dependencies together for easy portability.
Abstraction
An abstraction layer creates a unified interface that can be used instead of having to manage the complexities between individual cloud platforms. This can simplify interactions and reduce or remove the need to learn provider-specific interfaces and tools.
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
If different cloud providers have different protocols for user access and permissions, security controls can become complicated quickly. Identity and access management (IAM) solutions centralize permissions and user access between cloud providers to minimize risks associated with unauthorized access and reinforce consistent policies. Tools like Google Cloud Identity and Access Management (IAM) and AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) can better protect sensitive data.
Factors to Consider When Evaluating Multicloud Storage
Identifying the benefits, challenges, and tools to use in multicloud storage are just some of what you should consider when evaluating your options.
Complex Workloads
While multicloud storage can handle complexity with the right tools, if workloads have too many dependencies and run mission-critical applications, or require vendor-specific features, they may be a better fit for single cloud providers. More ideal workloads have minimal dependencies, such as web applications, content delivery networks (CDNs), and big data analytics.
Performance Needs
Performance needs to be weighed with the need to unify data via multicloud storage. If latency is of the utmost importance, multicloud may not be ideal because it can add latency with data transfers between clouds. Robust network connections are also necessary for high throughput – data transfers between cloud environments.
Data Security and Compliance Requirements
Security and compliance requirements can dictate the type of cloud environment that works best. You’ll want to check whether:
- The multicloud storage solution offers encryption for data in transit and at rest
- The solution complies with data storage regulations relevant to your industry
- You are able to control user access and permissions effectively and with enough detail across cloud environments
Existing Infrastructure Compatibility
When it comes to compatibility, your existing IT infrastructure needs to be able to accommodate dependencies and also have the networking, management tools, and APIs in place to handle multicloud storage. Can your network handle multiple transfers between clouds? Do you have the in-house expertise necessary to successfully manage a multicloud environment?
In-House Skills
Your IT team should have the following skills for managing a multicloud infrastructure. You either need skilled personnel onsite or available on-call to troubleshoot issues that may arise from different cloud platforms. The team you work with should also understand the ins and outs of different cloud providers and how to migrate workloads to a multicloud environment.
How Do You Implement Multicloud Storage?
Once you’ve weighed the benefits and challenges and considered how multicloud storage could meet your needs, it’s time to plan your implementation. Here are some suggested steps to bring multicloud storage to your organization.
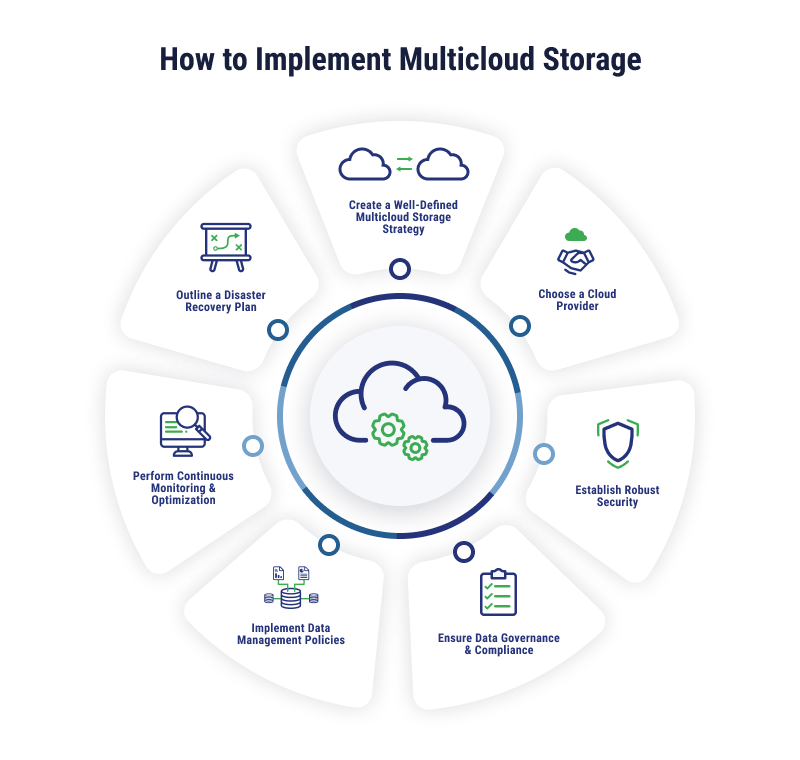
Create a Well-Defined Multicloud Storage Strategy
Adding a multicloud storage environment to your organization is beneficial, but any project needs to start by identifying the particular benefits for your business. Are you looking to apply different configurations to different workloads? Are you looking to scale more easily? Or do you just want to avoid vendor lock-in? Make your objectives clear in your strategy.
From there, you can evaluate your current workloads and compare features from different cloud providers. Which vendors will meet your needs and house your data most effectively?
Choose a Cloud Provider
When you’re evaluating cloud providers and choosing which to use, start smaller. You can always add more vendors over time. Your evaluation and selection should take into account different features and strengths that complement your needs. If your business is considering exiting and choosing a different cloud provider in a few years, you may want to go with a vendor that seems easier to walk away from concerning data migration.
Establish Robust Security
Because your organization will be working with multiple cloud providers, establish a consistent security policy that can be applied throughout your environment. This can be done by outlining cloud storage best practices, training employees, and unifying security measures with multicloud tools.
Businesses should also ensure their data is encrypted at rest and in transit. Cloud providers are responsible for infrastructural security measures, but often not for data security.
On a more granular level, organizations should implement identity and access management (IAM) controls to manage user permissions regardless of where the workload is housed that they are trying to access.
Ensure Data Governance and Compliance
Coinciding with security uniformity, businesses should also establish clear and consistent policies around data access, ownership, and retention policies. Compliance is another key part of strong data governance.
Some cloud providers may be compliant with necessary regulations relevant to your business or industry, and others may require additional configurations or safeguards to be compliant. Choosing cloud providers that have certifications relevant to your business can save you time and stress.
Implement Data Management Policies
Multicloud environments can introduce more complications, so data management policies are essential to keep your storage organized. Organizations should consider the following:
- How will data be replicated so that it is available from all clouds across devices?
- How will your organization deal with outages to ensure proper backups are being stored and redundancies are available? This can also include choosing backup locations that are geographically distinct.
- How will you create a data transfer strategy that optimizes performance?
Perform Continuous Monitoring and Optimization
Regularly review your multicloud storage solution to confirm that latency, resource utilization, and throughput are staying consistent. Optimize costs and adjust as needed to select more cost-effective storage options. Continue to monitor to find and address any security vulnerabilities before they become larger problems.
Outline a Disaster Recovery Plan
Even with the best plans, disasters can happen. Sometimes, these are natural disasters. In other cases, they can be human error. Protecting and recovering data after disasters should factor in weather, fires, human error, malicious insiders, ransomware, and more.
Determine the acceptable amount of downtime your organization can handle (recovery time objective) and how much data you can afford to lose (recovery point objective). This will dictate the steps you will take in a disaster recovery plan that responds to disasters and outages.
For disaster recovery plans to be effective in real-life events, it’s important to test them regularly, at least once a year. This can help solidify who is responsible for what when faced with an emergency and can highlight any deficiencies in your planning.
Need Help with Multicloud Storage Management?
Storage management in a multicloud environment can help organizations achieve the best of a few different worlds, but choosing more than one cloud for storage can also get confusing quickly. It’s easy to make the wrong decision when you feel inundated with options.
TierPoint’s IT advisory services can help move your organization from uncertainty to efficiency. Whether you have questions about the right cloud platform for your data, you’re looking for a data center, or you’re curious about creating a multicloud ecosystem, our team of experts can help you craft a solution that works best for you.

