May 3, 2024 | Channing Lovett
What is a Data Center Fabric? Unveil Scalability for Modern Needs

Traditional data centers are being put to the test with the rise in cloud computing, data-intensive applications, and virtualized servers, as well as the proliferation of artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI/ML) technologies. Data center fabrics offer a solution to meeting these new demands. By interconnecting resources using intelligent switches, like a data center fabric, businesses can create a dynamic, highly scalable environment that can change with evolving needs.
Below, we discuss what a data center fabric is, its components and types, and things to consider before using this approach in your business.
What is a Data Center Fabric?
A data center fabric consists of high-speed network connections that link storage devices and servers within a data center. The design of a data center fabric is meant to be scalable and flexible to overcome limitations and challenges associated with traditional data center network architectures.
How Does a Data Center Fabric Work?
Data can travel between different parts of the data center efficiently using switches, mesh-like connections, and a unified network. Switches connect together to route the network, mesh-like connections create multiple data paths between devices, and altogether, the pieces work as part of a unified network.
Different Types of Data Center Fabric Architectures
With increasing demand for fabric switches driving the market, there are a few different types of data center fabric implementations that you may choose, which all come with important advantages and considerations.
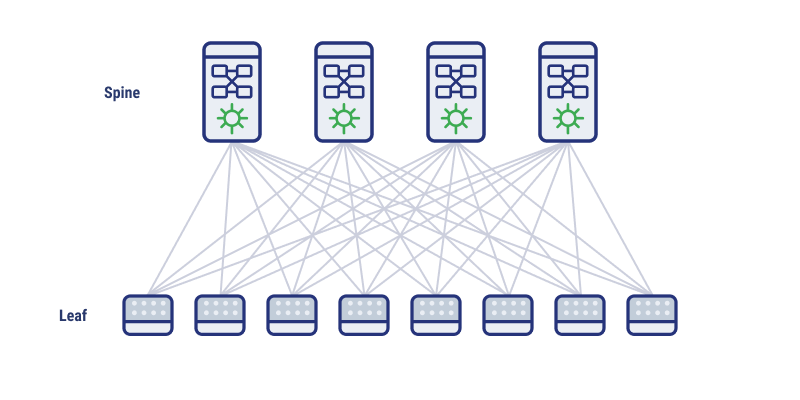
Spine-Leaf Topologies
Spine Leaf architecture generally uses two layers of switches. Leaf switches connect to storage devices and servers at the edge of the network and are sometimes called ToR (top-of-rack) switches. Spine switches interconnect the leaf switches, creating the mesh. This form of topology is generally easy to manage, simple to scale, and good for high-performance architecture.
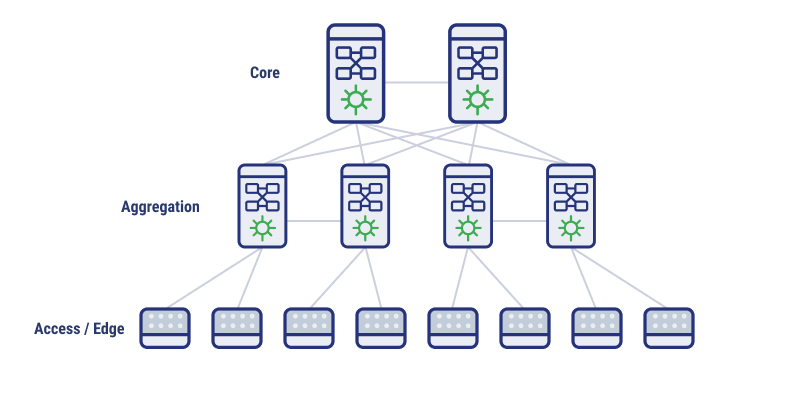
Traditional Three-Tier Architecture vs. Modern Fabric Architectures
As the name would suggest, a traditional three-tier architecture is an older network design with three layers. The access layer is where switches are connected to devices, such as servers, directly. The aggregation layer takes the aggregate traffic from the access layer and switches it. The core layer routes traffic between different subnets and serves as a central hub.
Comparatively, modern fabric architecture has more interconnected switches instead of a core layer. This allows for lower latency for east-west traffic, improved flexibility, and better scalability. Modern approaches remove common bottleneck issues and improve management.
Cloud-Ready Fabrics for Hybrid and Multicloud Environments
Modern data fabrics are not only easier to configure, they’re also cloud-ready for hybrid and multicloud environments. Cloud computing trends, such as AI-as-a-Service, real-time cloud, and the Internet of Things (IoT) are making cloud environments even more popular.
Fabrics can use technologies such as virtual extensible LAN (VXLAN) encapsulation and Ethernet VPN (EVPN) to make it easier for servers to be associated with each other in a data center without a physical connection, simplifying the management of multicloud and hybrid deployments.
Components of Data Center Fabric
To operate efficiently, data center fabric architectures rely on the following components.
Network Virtualization and Software-Defined Networking
While traditional networks can be rigid, network virtualization offers a rearrangeable maze for organizations to create multiple virtual networks on top of the same consistent physical network infrastructure. Software-defined networking (SDN) separates the control plane from the data plane, so the directions for the network and the flow of data can be managed with more flexibility.
These components are used together in data center fabrics to provision resources as needed, isolate network segments for certain workloads, and automate configuration tasks.
Fabric Switching and Routing Technologies
Switches are some of the most important pieces of data center fabrics because they allow for the multiple data paths that make fabrics great for performance. Even in moments of congestion or switch failure, fabric switching allows for lossless forwarding. Fabric routing determines which path, depending on available switches and latency concerns, will be the best to move data across the fabric.
Converged Infrastructure and Hyperconvergence
Converged infrastructure combines data center equipment into a single system, instead of having servers, storage, and networking arranged separately. These pre-built arrangements can be taken further via hyperconvergence, integrating the functionality of a combined system into software that runs on a standard server.
Understanding the Benefits of a Data Center Fabric
When organizations implement a data center fabric, they can enjoy simplified management, better performance and efficiency, and greater agility for scaling workloads later on. Networks can be reconfigured to meet changing needs quickly. High-bandwidth connectivity and multiple data paths decrease latency issues significantly. Data fabric architecture is also cloud-ready and allows for greater isolation of workloads, improving security.
Challenges and Considerations in Data Center Fabric Adoption
Before adopting a data center fabric configuration, businesses should consider the following:
- Integration with legacy systems: Existing data center infrastructure might not be immediately compatible with legacy frameworks. Doing so properly may require careful planning.
- Security/compliance concerns: While data center fabrics can improve security through isolation, they can also increase the number of potential attack surfaces. Carefully configure and engage in ongoing monitoring to ensure your environment is compliant with relevant security standards.
- Skill development: Teams need to be well-versed in software-defined networking, network virtualization, and fabric-specific protocols to create an effective framework. This may call for additional training or bringing in outside expertise
- Design considerations: Optimal performance depends on understanding traffic patterns, redundancy needs, and future workload growth projections. Design a fabric with the present and future in mind.
Is a Data Center Fabric the Right Choice?
Whether a data center fabric is the right choice for your business can depend on multiple factors. However, the following are signs that it may be time to consider adoption.
Greater Need for Scalability and Rapid Deployment
A fabric needs to support quick provisioning and scaling of new applications. A significant benefit that businesses get out of data center fabrics is the ability to scale new applications and virtualized workloads. AI/ML technologies put intense demands on computing, often requiring GPUs over CPUs. Scalability is necessary to support new technologies and enable further growth.
Increasing Requirements for High-Speed Data Transfer and Low Latency
Cloud computing, big data analytics, and real-time apps have little to no tolerance for latency. When the technology you’re using and the tools you’re building call for high performance, data center fabrics can deliver the speed you need.
Growing Security Concerns
On a global scale, ransomware is the “most immediate threat” we face, and small businesses are at just as much of a risk as larger ones. Data center fabrics can enhance network security and protect against these threats with features such as micro-segmentation.
Interest in Embracing More Cloud Benefits
Businesses that are ready to reap more benefits from the private cloud can enjoy seamless integration through fabrics. Cloud environments, themselves, allow for greater innovation, agility, and scalability with cost-effective pricing structures.
Ready to Elevate Your IT Infrastructure?
When it’s time to upgrade, implementing a data center fabric can feel like a lot to take on. TierPoint can help you elevate your infrastructure through our cloud consulting and IT advisory services. We’ll take you from a traditional structure to one that allows for maximum flexibility and innovation. Contact us to learn more.

FAQs
The primary purpose of a data center fabric is to serve as a scalable, high-speed network for servers and storage devices within a data center.
Data center fabrics improve data center performance and efficiency by offering multiple paths for data and high-bandwidth connections compared to traditional data center configurations.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) aren’t directly driving data center fabric adoption. However, fabrics can handle east-west traffic and cloud deployments that are common with AI/ML technologies.
