January 7, 2025 | Matt Pacheco
Building Your Cybersecurity Team: Best Practices for 2025

Cybersecurity threats will continue to grow and change in 2025, underscoring the importance of robust cybersecurity operations. A strong cybersecurity team can help safeguard sensitive information and protect against potential threats. We’ll cover the role of a cybersecurity team, top skills for professionals, and best practices that will ensure teams are fit to meet the challenges of emerging cyber threats.
Understanding the Role of a Cybersecurity Team
Cybersecurity teams safeguard a business’s digital assets. Their roles include identifying threats, responding to incidents, training employees in security best practices, and implementing measures to ensure data compliance and protection.
Roles & Responsibilities: Structuring a Cybersecurity Team
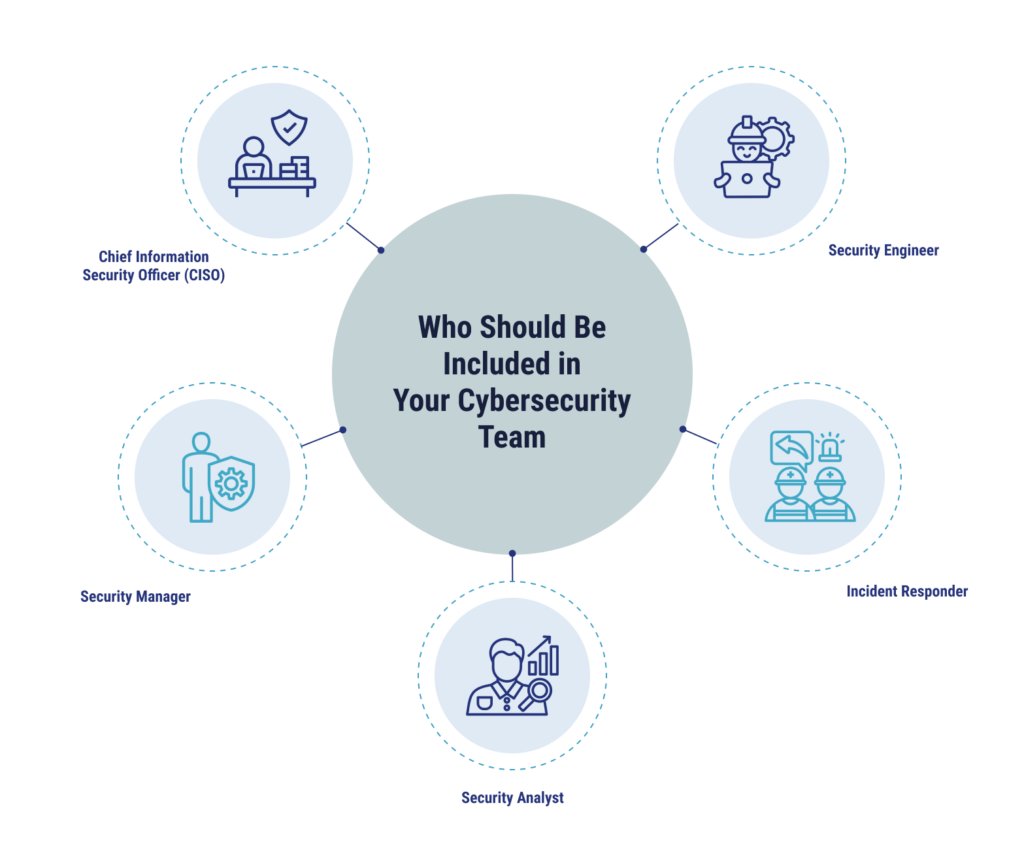
There are five essential roles and responsibilities a cybersecurity team must include in its structure:
- Chief Information Security Officer (CISO): The role of the CISO is to oversee the overall cybersecurity strategy of an organization. This professional should be proficient in risk management and understand compliance requirements.
- Security Manager: Security managers are concerned with the daily operations of the rest of the security team, overseeing access control, vulnerability management, and incident response for the organization.
- Security Analyst: These team members monitor for threats in a given environment, analyzing incidents and developing strategies to mitigate risks and plan actions for future attacks.
- Incident Responder: Should an incident occur, incident responders employ specialized skills to handle events like data breaches and ransomware attacks. They will coordinate response efforts, work quickly to contain breaches, and restore systems back to normal as efficiently as possible.
- Security Engineer: Security engineers design, implement, and maintain the security infrastructure for the organization. This can include intrusion detection systems, firewalls, and encryption technologies.
Creating an Effective Security Operations Center (SOC)
A well-organized Security Operations Center (SOC) can empower organizations to proactively address cybersecurity threats and reduce the risks associated with cybersecurity threats. A dedicated SOC can speed up incident responses, improve the security posture of a business, enhance capabilities associated with threat monitoring, and facilitate collaboration among members of a security team.
The necessary roles for a SOC team can often be intertwined with a core cybersecurity team, but depending on the size of the organization, they can be distinct. Some roles that may overlap include the SOC manager, incident responder, and security analyst.
SOC teams also often have a threat intelligence analyst and a communications and public relations specialist. A threat intelligence analyst gathers and disseminates threat intelligence to develop further in-house proactive security measures. Communications specialists handle communications both internally and externally during security incidents. This can include informing the public, key stakeholders, and internal team members about how to handle an incident or what steps are being taken to resolve the problem.
Top Skills for Cybersecurity Professionals
To create a thriving cybersecurity team that effectively protects an organization, professionals must possess a mix of technical skills, analytical skills, and personal attributes.
Technical Skills
- Network security: Cybersecurity team members need to have a deep understanding of network architecture, protocols, and security best practices. This includes knowledge of firewalls, intrusion detection systems, intrusion prevention systems, and virtual private networks (VPNs).
- Cybersecurity frameworks and standards: Cybersecurity standards change frequently, and cybersecurity professionals need to keep themselves up to date with the latest frameworks, such as the NIST Cybersecurity Framework, ISO 27001, and CIS controls.
- Cloud security: Many organizations are moving some or all of their workloads to the cloud, and these environments present new security challenges. Cybersecurity teams need to have skills associated with cloud security, particularly those that align with your cloud provider of choice.
- Incident response: Team members should be experts in incident response methodologies, threat hunting, and digital forensic approaches.
- Cryptography: Which cryptographic algorithms and communication protocols are required to protect sensitive data?
Analytical Skills
- Problem-solving: To properly identify, diagnose, and resolve security issues, cybersecurity team members need to be natural problem-solvers.
- Critical thinking: It may be necessary to extrapolate from what you know to evaluate a more complex situation and make a well-informed security decision.
- Attention to detail: Both through the configuration and monitoring of tools, cybersecurity teams need to be meticulous in their attention to detail.
Personal Attributes
- Continuous learning: As the cybersecurity landscape continues to change, cybersecurity team members need to be committed to a state of continuous learning. Consider requiring regular training and certifications for incident response, SOC operations, and information security.
- Communication skills: For a team to work cohesively, every member needs to communicate and collaborate effectively. They also need to be able to communicate with stakeholders and clients.
Tools and Technologies for Cybersecurity Teams
Team members need to have the right skills, but they also need to have the proper tools in place to protect organizational assets.
Essential Cybersecurity Software and Tools
The software and tools used by cybersecurity teams will typically align with the actionable steps outlined by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework (CSF). These can include:
- Multifactor authentication
- Data loss prevention
- Next-generation firewall
- Email protection
- Intrusion detection systems
- Antivirus and anti-malware software
- Log management
- End user education
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
Tech Stack Considerations
When building a tech stack with these tools in mind, an organization should make choices based on budget, as well as current and future needs. This may include finding tools that scale easily, integrate well with existing systems, have user-friendly interfaces, offer desirable security features, and provide cost-effective solutions to an organization’s most pressing security concerns.
Best Practices for Optimizing Cybersecurity Team Performance
Cybersecurity teams face several challenges in the digital age, including more sophisticated and targeted attacks, resource constraints, and changing regulatory standards. To address these challenges, teams must take a proactive approach to cybersecurity, stay informed about the latest threats, and invest in advanced security technologies that can counter the most common incident types and vulnerabilities.
Having a clear framework and protocols in place can help cybersecurity teams perform to their fullest potential. Sometimes, optimizing performance will include working with a trusted security partner who can fill in key skill gaps and augment existing teams.
Developing Strong Security Policies
Developed policies should include:
- Acceptable Use: Guidelines on how technology resources should be used, and what constitutes misuse
- Access Control: Who needs access to which resources, and which circumstances will change the level of access
- Data Classification and Protection: Safeguards for data, classified by sensitivity level
- Incident Response Plans: Procedures for how security incidents will be addressed
- Passwords: Standards for password complexity and required frequency for changing credentials
- Remote Access: Secure remote access guidelines for VPN usage and other devices
Incident Response Planning and Management
No cybersecurity team should be scrambling when an incident occurs. Creating an incident plan is the first step. It’s also important to test it to ensure that when it is needed, it can be carried out successfully.
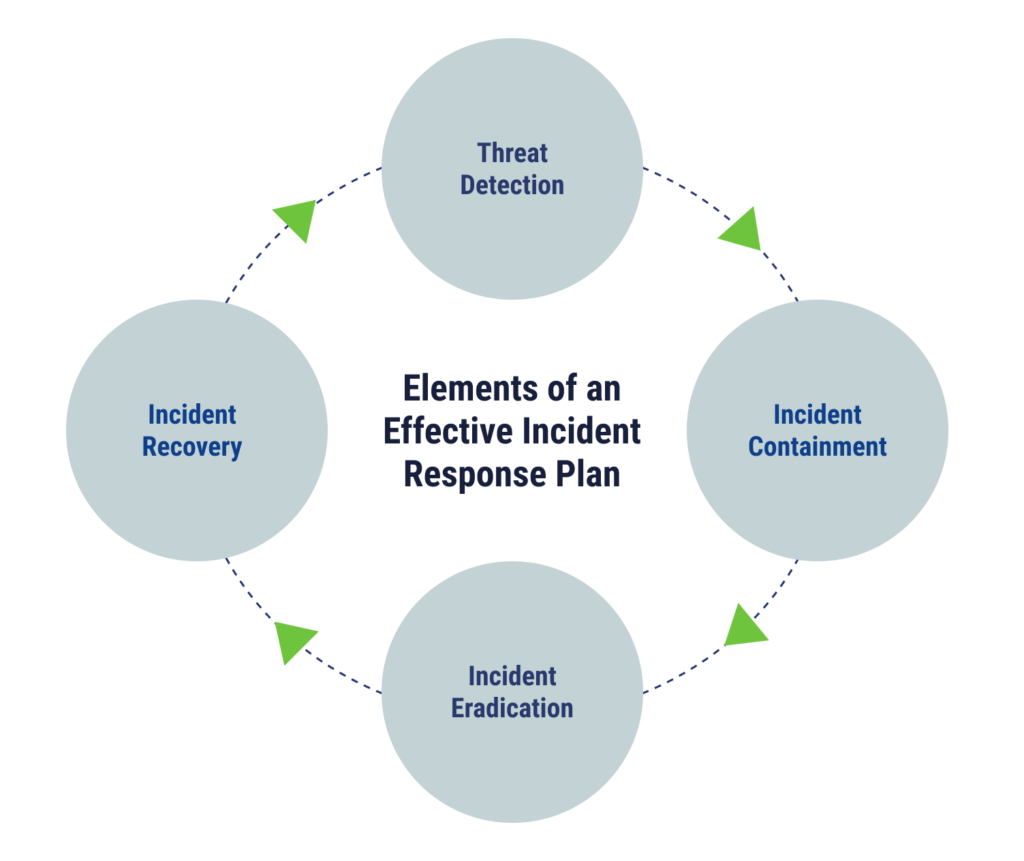
An effective incident response plan will include steps for threat detection, incident containment, incident eradication, and incident recovery. In essence, cybersecurity teams should have an established plan for how to deal with incidents and how to get systems back to normal without experiencing excessive downtime or data loss. Incident response management should also include a post-incident analysis, where the team collects lessons learned that can be applied to future response efforts.
Continuous Monitoring and Risk Assessment
Continuous monitoring and risk assessment can reduce the frequency of events to begin with. Cybersecurity teams should be performing continuous network security monitoring to find signs of potential malicious activity. They should also be protecting endpoints with firewalls, anti-malware, and antivirus solutions. New vulnerabilities are uncovered regularly, underscoring the importance of scanning for these vulnerabilities and testing the strength of system defenses in the face of simulated attacks.
Choosing a Trusted Security Partner
In the face of so many different threats, it’s clear that managing cybersecurity is a full-time job that could occupy the time of several team members. Often, these are more resources than an organization has at its disposal. Plus, with two-thirds of technology leaders facing internal skills gaps, many organizations are contending with a pipeline that won’t fulfill all needed skills any time soon.
Working with a trusted security partner, like TierPoint, can help businesses close their skill gaps with cybersecurity experts who are available for important planning stages, management tasks, and critical, time-sensitive moments.
Future Trends & Planning for Cybersecurity Teams
What are some threats cybersecurity teams may have to face in the coming years? The rise in automation, AI, and remote work has posed new challenges for cybersecurity teams, but developing a strong, proactive cybersecurity culture can help organizations stay one step ahead of attackers.
The Rise of Automation and AI in Cybersecurity
Automation and artificial intelligence (AI) are bringing new changes to the cybersecurity landscape, both in how attacks are shifting and how businesses can use technology to respond to these attacks. AI-enabled technologies can offer advanced threat detection and automated incident response. Teams can even use security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR) platforms to automate repetitive tasks and improve security operations overall.
Remote Work and Its Impact on Cybersecurity Teams
Remoter work models can be more vulnerable to cyberattacks due to their distributed networks and the use of personal devices for work tasks. However, cybersecurity teams can counter these issues through strong remote access policies, such as requiring multifactor authentication or access through specific devices. Remote monitoring tools can also be used to assess the security posture of remote devices being used for work.
Developing a Proactive Cybersecurity Culture
Remote and in-person teams can both benefit from employee training and a proactive culture around cybersecurity. This requires strong leadership buy-in that echoes the commitment to cybersecurity measures and prioritizes time for employee awareness and training for all departments. Cybersecurity teams can facilitate regular training, incident response drills, and continuous learning opportunities for team members so that even those who work outside of security contribute to the culture of proactivity needed to make cybersecurity efforts more successful. Additionally, educating employees on handling sensitive data—like spotting phishing, securing credentials, and avoiding risky behaviors—helps minimize vulnerabilities and fosters a resilient cybersecurity culture.
Ensure Your Cybersecurity Team Is Set Up for Success
Staying current with the latest knowledge is a lot for most cybersecurity teams to handle. By trusting and partnering with experts, like TierPoint, cybersecurity teams can receive customized security consulting that improves business resiliency and greatly reduces the risk of cyber threats.

