April 4, 2024 | Channing Lovett
How Air-Gapping Backups can Strengthen Ransomware Protection

Data backups provide a level of security for businesses looking to improve their resiliency and ability to handle any disasters or intrusions that may come their way. However, not all backups are created equal. Traditional backup methods can help businesses by providing an additional site to store their data should their main environment go down, but these run the risk of being accessed by cybercriminals, just like any main system.
By air-gapping backups, businesses can protect their data in a distinct way, physically or virtually isolating their data from any online access. We’ll cover what air-gapped backups are, what sets them apart from other methods, why they’re important for resilience, and what to consider before implementing them in your IT security plan.
What are Air-Gapped Backups?
Air-gapped backups create distance between critical data on your computers and the internet. When your data is air-gapped, the separation makes it unable to be accessed by cybercriminals and malware which typically use online channels. By air-gapping devices, businesses can create an additional layer of security and greatly improve their likelihood of making it through a data breach or other disaster.
Why are They Important for Security and Resilience?
When businesses create a virtual layer between devices and the internet, this separation allows air-gapped data to operate in isolation from threats that pose a risk to data security. In 2023, 82% of data breaches originated from data stored in the cloud, either public, private, or hybrid. By creating air-gapped backups, businesses can improve their data protection approach and become more resilient.
How Do They Work?
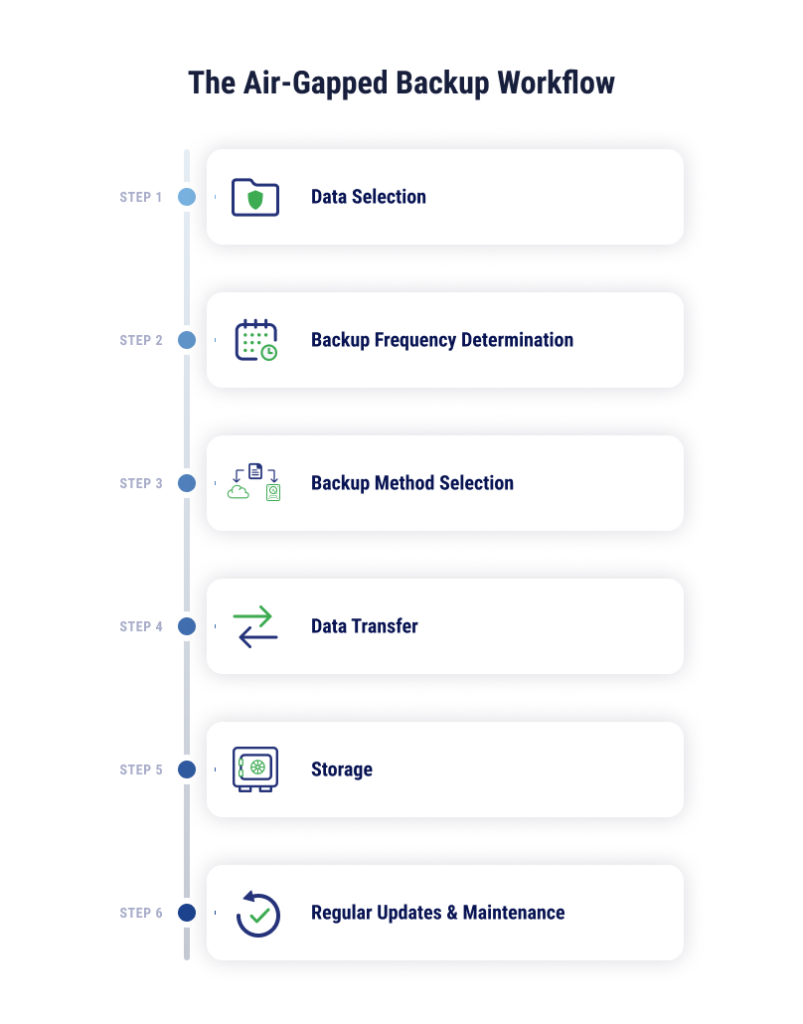
Air-gapped backups work by using a separate storage system to be either virtually or physically separate from the main environment. Based on how frequently your data updates, and how critical it is to have extremely current data in a backup environment, your business will choose how often data will be transferred and updated in the backup environment. Traditionally, this looked like backing up data on tapes and storing them offline. Even when air-gapped data is stored in the cloud, the network the data is stored on would be offline, making this method distinct from other backup solutions.
Types of Air-Gapping Backup Methods
There are three types of air-gapping backup methods businesses may employ: physical, logical, and cloud.
Physical
Physical air-gapping is a traditional method for backing up data in a physically isolated environment. The method involves moving the data and isolating backup storage from any physical connection that would allow it to be accessed by outside actors. Physical air-gapping can include removable storage devices, such as external hard drives and tapes, or specialized hardware backup devices that generally come with built-in network isolation features. Backup devices like these can usually automate backup processes to cut down on the manual effort businesses may need to take on with tapes or hard drives.
Logical
A less labor-intensive method businesses can try is employing logical air gaps. Instead of creating a physically distinct environment, logical air gaps rely on software and network segmentation to separate the storage from the network. Even if storage devices are physically connected to a network, this method can put up a virtual barrier that blocks access from the internet.
Cloud
Cloud air gaps are similar to logical air gaps, with some organizational differences. Logical air gaps can exist within the business infrastructure, for example, while cloud air gaps live on a infrastructure that is ultimately controlled by cloud providers.
While IT teams may be able to implement immutable functionality, such as object locking and isolated network segments within the cloud, the environment is ultimately dependent on the practices of the cloud provider.
Businesses should understand the level of security and isolation cloud providers offer before deciding whether this is an appropriate method for their needs.
What Common Ransomware Threats Target Data Backups?
Data backups are a prime target for cybercriminals. Ransomware attacks can involve backups in a few different ways, including backup encryption, backup software vulnerabilities, and credential theft.
Ransomware attacks are not limited to the encryption of primary data. Cybercriminals may also seek out connected backup drives and encrypt them as well. If bad actors can get into your backups, that leaves your business unable to restore your data from a secondary site.
Credential theft involves stealing login credentials, which could be logins for the production environment, backups, or any other door criminals may be able to unlock. Stolen credentials are one of the top two initial attack vectors used by criminals.
Known vulnerabilities in software are especially dangerous in the days before they are discovered and patched by companies. Ransomware attackers can use these known vulnerabilities to gain access to your systems, including your backups. Maintaining a regular patching system is one way to keep these risks low, but if there is any network access to backups, attackers may get in.

How Do Air-Gapped Backups Provide Ransomware Protection?
Critical data is not just valuable to your organization, it’s also an attractive target for cybercriminals. Ransomware will encrypt your high-value data, and if it infiltrates your backups, you’ll be left without a clean backup copy that you can use to restore your systems. Air-gapped backups provide ransomware protection through encryption, hashing, network isolation, offline storage, verification, and maintenance of data integrity. Some of these features can help with prevention, whereas others will lend a hand with ransomware remediation.
Encryption and Hashing
Air-gapped systems already offer a significant level of protection for businesses due to their offline nature. Encryption and hashing increase these security benefits, making the data unable to be deciphered even if hackers end up gaining access. Hashing algorithms bolster data integrity by ensuring that backups haven’t been accessed or altered during the transfer process, so your data can be more secure at rest and in transit.
Network Isolation from Cyber Threats
It’s worth reemphasizing that one of the biggest strengths of air-gapped backups is the disconnection from the network offered by this approach. By making your backups out of reach, hackers are not able to encrypt, let alone access, your critical systems.
Offline Storage
Offline storage offers a highly reliable recovery point for businesses after they experience a ransomware attack. When backups are stored offline, they’re out of reach of malware and encryption tools that can spread through a network.
Data Integrity and Availability
Air-gapped backups make restoration more efficient and reliable by improving data integrity and availability. Because air-gapped environments have robust access controls, or are even physically isolated from the rest of your data, accidental tampering and deletion are highly unlikely. When it’s time to restore data from your air-gapped backups, availability is predictable and reliable, whether it’s stored in the cloud or on physical equipment. This allows you to get back to your daily processes quickly
Verification and Monitoring
Organizations can detect potential ransomware attacks on backup data stored in air-gapped environments by implementing anomaly detection and monitoring access logs. Even when environments are physically isolated, suspicious activity can occur, so maintaining monitoring and detection tools is critical to enhancing your overall cybersecurity resilience within and outside of air-gapped environments.
Access Management
Just like monitoring and verification tools can make your backups that much more secure, access controls are an essential part of boosting the security of your air-gapped systems. Provide authorization only to team members who need to manage the backups regularly and require multi-factor authentication for access. Add one-off authentication when necessary to keep ongoing access points low.
Things to Consider Before Using Air-Gapping Backups in a Recovery Plan
While improved data protection can sound like a great reason to go all-in on air-gapped backups, adding this approach to your business continuity planning shouldn’t be initiated until you consider the following factors.
Data Accessibility
Because of how isolated air-gapped backups can be, they’re also less accessible compared to traditional online backups. If you’re looking for a backup method that offers easy access for regular tasks, or you need to perform a quick restoration of a file or folder, air-gapped backups are not the best fit for these purposes. Pair the type of data you’re looking to back up with the approach that will offer the right level of accessibility.
Physical vs. Logical vs. Cloud Air-Gapping
Physical, logical, and cloud air-gapping methods each have their pros and cons. While physical air gaps can offer substantial isolation, they require more effort to access and restore. Cloud air gaps can be the most convenient, but the isolation isn’t as strong compared to logical and physical methods. Understanding the benefits and drawbacks of each will allow you to choose a method that will work for your needs and security posture.
Backup Frequency and Retention
Backups go from useful to worthless if there’s too much time between saves. Frequent backups allow for a more recent recovery point, meaning you’ve lost less of your recently saved data. However, this also requires more storage and management to configure and run. Use your recovery point objectives and recovery time objectives to determine your frequency and retention periods.
Backup Testing and Monitoring
Setting up air-gapped backups is only one part of the process. You need to regularly test your backups to ensure that they will successfully restore your data in the event of a ransomware attack or other breach. Make sure that testing and monitoring are part of your regular tasks.
Integration
What do your existing ransomware recovery processes look like? Your air-gapped backups should be able to integrate well with your existing systems so you can securely transfer data to and from this new environment. If this will require some work to coordinate, consider the time and resources it will take when developing your strategy and budget.
Costs
Any new method you add to protect your data will cost additional money for hardware, software, and perhaps even offsite storage if you choose to incorporate physical media. Consider these costs in your overall IT budget to determine what level of support you can maintain.
Building a Resilient Shield Against Ransomware
Every tactic you add to your data protection strategy will make your shield against threats like ransomware more and more resilient. TierPoint’s approach to ransomware includes air-gapped backup solutions, vulnerability management, security consulting, and other business continuity and data security measures. Learn more about ransomware’s impact on businesses and what you can do to improve your security posture by reading our eBook.
Learn more about our Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS) and other solutions that can mitigate ransomware’s effects. Download our infographic to learn 13 steps to creating an effective disaster recovery plan.

FAQs
The difference between air-gapped and immutable backups is primarily about the focus of the technology. Immutable backups are mostly concerned with data integrity, whereas air-gapped backups are focused on the physical separation between the data backups and any network connections.
The purpose of an air-gapped backup is to provide a physically isolated location for critical data that is not connected to the internet. By being disconnected from the network, businesses can use air-gapped backups as a final line of defense from incoming threats.
Businesses can create air-gapped backups by choosing a method – physical or logical – and applying a process to collect data, create the backup, and save the data offline. Physical backups can be more secure but also take more time compared to logical backups.
