July 31, 2024 | Matt Pacheco
Data Center Interconnection: What is it & How Does it Work?

Is data center interconnection the missing link in your data center strategy? Whether you’re looking to improve business continuity or help bring data processing closer to your users, you can stand to benefit from data center interconnection. Connecting your data with other centers across the country can help you achieve your digital transformation or business goals and better serve your customers. If you’re looking to adopt a hybrid cloud strategy, improve business continuity or disaster recovery, or if you want to move your IT infrastructure from your onsite data center to a third-party provider, you could benefit greatly from data center interconnection.
What is Data Center Interconnection?
Data center interconnection (DCI) is dedicated network connectivity that spans your data centers, permitting your apps, data, and users to connect reliably and quickly. With interconnection services, data center facilities offer services where customers can connect between various facilities across a regional or nationwide network.
If you work with a provider that offers data center connectivity, resources can become available closer to your users via private lines, ethernet, and fiber waves. This decreases latency and improves your users’ internet service experience. While the focus used to be on connecting first-tier markets, many centers can directly connect to second- and third-tier markets as well. At any of these locations that are interconnected, you’re also likely to have support available for all assets under one roof, including a colocation data center, cloud services, and network assets. Plus, when you’re looking for processing and coverage in specific geographies, you can choose providers that have data centers closest to your users.
Objectives of Data Center Interconnection
Businesses that choose interconnected data centers are likely trying to fulfill one or more of the following objectives:
Access
Interconnection enables connectivity with more internet service providers (ISPs), greater provider flexibility, and an increased ability to reach new markets and set up new customer bases. If companies are looking to geographically expand their offerings, an interconnected data center in ideal markets can help improve access.
Accessibility also extends to the list of cloud providers and partners data centers may have available in their facility. The ecosystem of partners can help businesses access specialized resources and services that they can integrate into their applications more easily.
Convenience
When data centers are interconnected, data transfer becomes more streamlined, reducing complexity and simplifying the network management process. Businesses can also scale up processing power and storage on-demand with an interconnected data center.
Interconnection
Because interconnected data centers establish direct connections with other facilities, data transfer latency, bottlenecks, and congestion are greatly reduced. This allows for a more reliable user experience. Applications that require real-time data exchange benefit greatly from lower latency, including high-performance computing, online gaming, and financial trading.
Cost
Shared resources can also help reduce costs for data centers and business customers. Interconnected data centers share resources and reduce the need for duplicate infrastructure, as well as cutting down on bandwidth charges from ISPs because of a decreased reliance on public internet connections. If there is a disaster, interconnection can also make the process of switching over to a new data center efficient and cost-effective, decreasing the impact from lost revenue resulting from downtime.
Disaster Recovery
By enabling high-bandwidth, low-latency connections between geographically separated data centers, data center interconnection facilitates a few key disaster recovery (DR) strategies. DCI allows for mirroring of critical data between sites. This means replicating your data in real-time or near real-time to the secondary location. If a disaster strikes your primary data center, the mirrored data at the secondary site remains readily available for recovery. Beyond data availability, DCI also allows for the utilization of processing resources from the secondary data center. With a DCI connection, you can seamlessly failover critical applications to the secondary site during a disaster.
Why Data Center Interconnection is Important for Businesses
Data center interconnection is important primarily because businesses are reliant on greater access, convenience, and connectivity to operate up to end user standards, all while keeping costs within budget. Interconnected data centers can help businesses meet evolving demands, improving reach, enhancing performance, boosting reliability, and offering greater convenience for businesses and users alike.
Benefits of Data Center Interconnection
Interconnection provides a beneficial environment for businesses looking for reliable, fast connectivity in a safe environment. Outside of the listed objectives, DCI comes with several other benefits.
Direct Connectivity is Faster and More Reliable
Bypassing the public internet makes direct connectivity faster and more reliable compared to data centers that are not interconnected. Users enjoy quicker speeds and a more reliable user experience because there are dedicated pathways available for data transfer. Additionally, many data center interconnections are part of a fully redundant matrix of circuits providing resilience during a specific circuit outage.
Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
Downtime can be expensive, and relying on a provider that doesn’t have contingency plans for outages and downtime can be costly for your business.
DCI can make data centers more resilient and well-equipped to handle disasters. For example, you can survive carrier outages unscathed if the center you’re working with is connected to other facilities, has buildings designed to withstand disaster, and has plans to offload data to another center should something unforeseen occur.
Scalability and Flexibility
Instead of having to purchase additional physical equipment or rely on outside resources, businesses can quickly access additional storage and processing power from their interconnected network. This allows for better flexibility with changing needs and enables on-demand scaling.
Improved Security
Interconnected data centers also have an improved security posture thanks to private, dedicated connections between data centers, making the connectivity much safer than public internet.
Cost Efficiency
Resource sharing and DCI go hand-in-hand, and interconnection can help reduce reliance on public internet bandwidth, resulting in cost savings and optimized IT spending.
Key Components of DCI Architecture
A few essential components make up DCI architecture, including networking, virtualization, physical connectivity, cross-connects, and more.
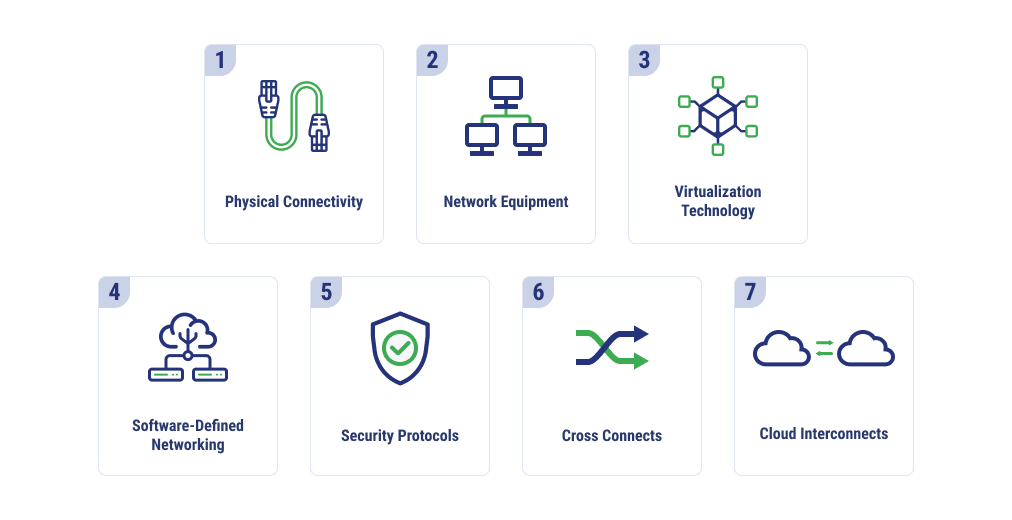
Physical Connectivity
Interconnection, at the base, requires physical connectivity. Fiber optic cables are a common choice for DCI because they can transmit data over long distances and have high bandwidth. Single-mode fiber might be used for longer distances, while multi-mode can connect at shorter distances.
Network Equipment
Network equipment includes routers, switches, and other networking devices that make data transfer possible. Switches make connections within a data center and routers work between data centers. Firewalls are also added to filter incoming and outgoing traffic, boosting security.
Virtualization Technology
Hypervisors, such as VMware ESXi and KVM, can create multiple data centers on top of physical resources. Virtual machines (VMs) abstract physical resources like storage, memory, and CPU. Virtualization can improve scalability, resource utilization, and manageability.
Software-Defined Networking
Software-defined networking (SDN) decouples the control plane that configures the network from the data plane that forwards data. This allows for greater network configuration flexibility and programmatic control. Organizations can more easily implement new features and functions with the help of SDN, as well as automate and enjoy greater network agility.
Security Protocols
In addition to network firewalls, other security measures can be added as part of DCI. AES-256 is an encryption protocol that scrambles data in transit, ensuring that data is kept confidential when transferred. Data centers may also add access control mechanisms to prevent unauthorized users from accessing certain workloads, or authentication protocols to verify the user’s identity when trying to access or send data. Facilities should also implement physical security controls.
Cross Connects
Cross connects create the physical links between different network providers between data centers, as well as equipment within a single data center. These connections are why DCI can be more secure and controlled compared to reliance on external service provider networks.
Cloud Interconnects
On-premises data centers can also be connected to cloud platforms through cloud interconnects, forming a link between public and private cloud environments or enabling other hybrid cloud deployments.
Achieve Resilience and High Performance with a Data Center Provider
As a data center provider, TierPoint offers all of the interconnectivity businesses need to effectively run their IT environment, no matter your needs. We offer a full suite of data centers across the U.S., so wherever your users are, we have them covered.
Are you wondering what building a data center on-premises vs. off-premises would cost? Check out our Data Center Build vs. Buy calculator.
FAQ
A: Data center interconnection (DCI) is different from hyperscalers because of their structures. DCI connects data centers to share resources, whereas hyperscalers are cloud providers, such as AWS and Azure, that offer their own cloud services.
A: Data center interconnection uses direct, high-bandwidth connections to reduce latency. This can include using dedicated lines, closer data centers, and fiber optics.
Businesses can test data center interconnections with active testing tools, passive monitoring tools, and cloud-based testing services. Active tools such as Spirent Landspeed and iPerf3 can measure performance through generated traffic. Passive monitoring tools like MRTG and PRTG can observe current traffic performance.

