
Microsoft 365 is the main collaboration platform used by businesses of all sizes across the world, hence why following Microsoft 365 backup best practices are so important. Backing up your 365 data isn’t just a good IT practice in the event of a “worst case” scenario – it’s a necessity within many organizations with board-driven and compliance-driven policies. After all, how would your business be impacted if your data or your customer’s data was suddenly inaccessible, lost, or compromised? How long can you afford to be down? What would you do if you were able to recover your data after a disaster, only to discover it was an old backup that was made weeks ago?
Unfortunately, no organization is immune from intentional or unintentional data loss. Ransomware attacks, internal malicious activity, innocent human error, or hard drive failures can all lead to critical data loss. Understanding what’s covered by Microsoft, and what’s your responsibility to protect, is a crucial first step toward stronger data backup practices and ensuring data resiliency in important moments.
What Can Be Backed Up from Microsoft 365?
Before we dive deeper into why backing up your data is important and some best practices, let’s examine the types of data that can be backed up from Microsoft 365.
Emails
Exchange Online can be backed up, including mailboxes, email attachments, folders, tasks, contacts, shared mailboxes, and calendars.
OneDrive
All files and folders under OneDrive for Business can be backed up.
Teams
All channels, files, chats and tasks should be included in backups.
SharePoint
Document libraries and site collections, as well as views, lists, and permissions, can all be backed up.
Why Traditional On-Premises Backups Are Not Enough
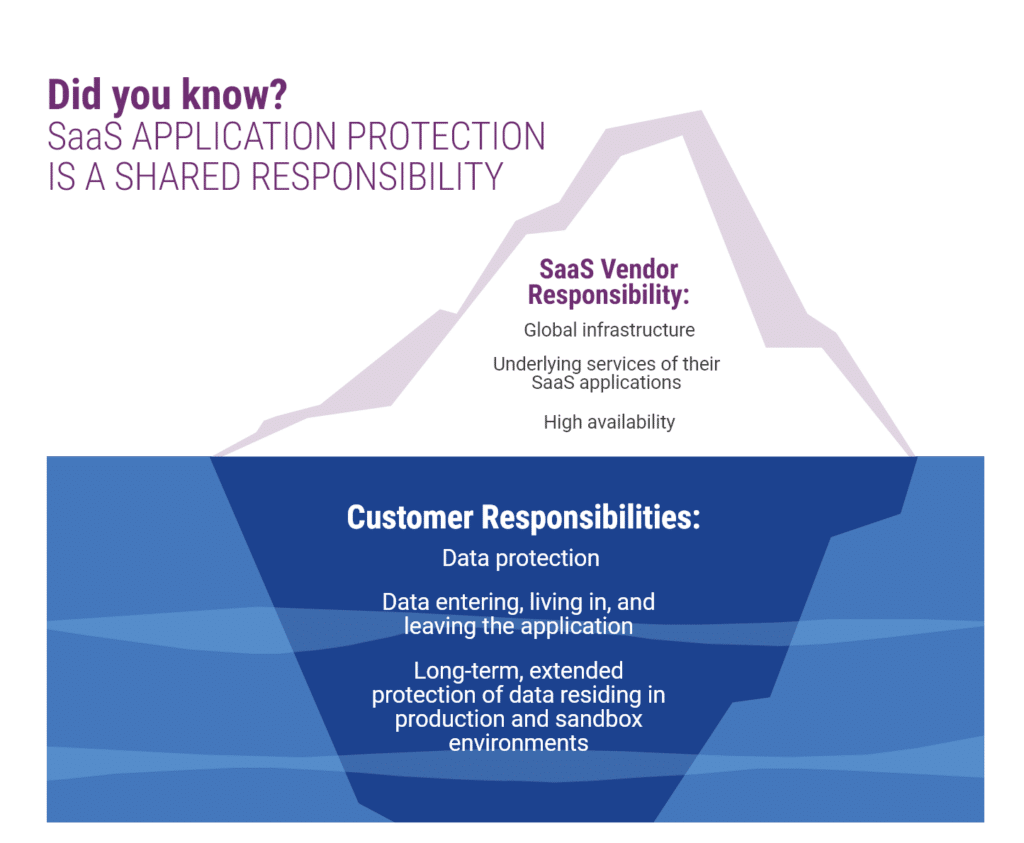
Organizations may think they’re covered by their SaaS vendor, such as Microsoft, and not have a need for backup and recovery services outside of the vendor. However, that’s not the case.
Microsoft operates according to a shared responsibility model. Under this model, they’re only in charge of ensuring their applications are working and their global cloud infrastructure is secure, along with:
- Basic data replication
- Maintaining privacy
- Regulatory controls
Even though infrastructure management is Microsoft’s responsibility, the customer still needs to prioritize data protection. Why? Because it’s your (not their) responsibility to ensure your data is safe from accidental deletion, intentional modifications that need to be reversed, corruption, or malicious attacks, among others.
Why Microsoft 365 Backup Is So Important
Rather than relying on Microsoft’s duties within the shared responsibility model, handling the task of backing up your data, whether its in-house or via a managed service provider, is important for several reasons, including:
- Protection against data loss: Accidental deletion, malicious actions, time-sensitive retention policies, and external threats can happen in the blink of an eye. The result? Data loss. Sticking to these Microsoft 365 backup best practices and regularly backing up your data can easily help you recover lost data or recover corrupted data from its original state.
- Meeting compliance requirements: Depending on your industry and location, you may be required to meet specific compliance regulations for data protection, retention, and recovery. Backing up your data can help you meet these requirements and avoid potential legal or financial penalties.
- Ensuring business continuity: The ability to access and work with your data is critical for business operations. If a disaster or outage occurs, up-to-date backups can minimize downtime and enable your team or customers to continue working with minimal, if any, interruptions.
Best Practices for Backing Up Microsoft 365
Need help getting started with backing up Microsoft 365? Here are eight Microsoft 365 backup best practices to keep top of mind when developing your plan of action.
Set Automated Backups and Backup Regularly
The risks we previously mentioned, including ransomware attacks and accidental or purposeful deletion, can be countered with backups, and the more automated and frequent the backups are, the easier it will be to restore to a point where less business data is lost. This schedule can be based on the frequency of data changes in your organization, like, how often users make changes in OneDrive – is it daily?
As a general rule of thumb, backing up your data daily is never a bad idea. However, most backup and recovery solution providers recommend making multiple backups a day. For example, TierPoint’s Microsoft 365 Backup and Recovery solution continuously backs up the customer’s Microsoft 365 environment with the goal of completing at least one incremental backup per 24-hour period.
Allow Versioning
With versioning, you can keep previous versions of documents and files even after deleting or editing them. You don’t have to worry about saving multiple files if you think you might need to revert back to a previous version. Microsoft 365 offers this as a native feature, but there are limits to how many versions can be captured, plus storage is dependent on the free space available. It may be important for your organization to invest in additional storage space to keep multiple versions.
Calculate Storage Space & User Data
Estimating what’s required for storing backups on a daily, weekly, or monthly basis is important. You can start this process by looking at how much storage space each user takes up in a given period of time and extrapolating from there. This can be done with app usage reports, a monitoring feature available in Microsoft 365.
Configure Retention Settings
When items are deleted and relegated to the Recycle Bin, they can be retained for a maximum period of 93 days. However, if what’s stored in the Recycle Bin goes beyond the storage quota, which is 10% of OneDrive storage or 50% for a site collection bin in SharePoint, more items will be deleted sooner.
Adding a third-party backup and recovery functionality on top of existing Microsoft 365 settings can help you tailor retention policies at your organization, so you don’t accidentally lose something important before you’re ready to delete it. It’s important to note that certain MSPs charge a rate per user’s storage requirements, so, if a user exceeds their storage, you may find yourself with a higher-than-normal bill.
Backup Security and Redundancy
When creating backups, don’t just store them on production servers or on OneDrive. Instead, store your backups in separate and secure, redundant locations to build an air gap and ensure data isolation. Whatever your backup storage destination(s) –whether on-premises, a third-party data center, cloud, or a mix — be sure its encrypted and protected from data corruption and data leaks.
Granular Recovery
It wouldn’t be unusual to need to recover specific items from a backup and not everything under the sun, and granular recovery allows for just that. Save time by only restoring specific data from a backup and gain more flexibility with Microsoft 365 recovery.
Routinely Audit Backups
Mistakes happen even to the best of us and when a cyberattack happens, you want to minimize any fumbling on the way to data recovery. With that, it’s important to perform regular restoration tests of your mission-critical data backups to ensure things are working correctly and that your files have not been accidentally (or intentionally) corrupted.
Object-Level Immutability
Immutable storage features are meant to maintain data integrity and keep anyone from deleting or editing data during a given period of time. This can even extend to systems administrators. An added bonus of doing this is that it can protect companies from ransomware attacks, preventing cybercriminals from being able to encrypt data and corrupt files.
Why Microsoft 365 Backup Best Practices and Tools Will Help
Easy File Access
Keeping a backup in a dedicated cloud environment will ensure that everyone in your organization has easy access to your data even if Microsoft 365 is down. Administrators can simply log in to the online backup service for quick file recovery.
Ease of Use
If your business is relying on manual backups, it’s easy to miss them. The day can get away from the person managing them, they get distracted, and before they know it, a day goes by without a backup having completed. Microsoft 365 has configuration options for e-Discovery backups, for example, but they aren’t automated or as sophisticated as a third-party dedicated backup solution.
Using a third-party backup service can help you rest assured that it’s working in the background as you set your sights on other things. Regularly send backups to the cloud or local storage without anyone in your organization having to lift a finger.
Improved Efficiency
Using a comprehensive backup and recovery solution can help you streamline your backup and recovery operations, reduce manual intervention, and automate routine tasks. This can help you save time and resources, and focus on more strategic business initiatives.
Choose The Best Backup and Recovery Approach With TierPoint
Investing in cloud-based backup and recovery with TierPoint means that our solution can quickly manage backup policies and store data cost-efficiently. Partnering with TierPoint ensures your organization won’t be overburdened when it comes to ensuring data security and regularly backing up critical data. TierPoint’s Microsoft 365 Backup & Recovery service can:
- Automate your backup and recovery process
- Reduce downtime
- Accelerate recovery
- Mitigate ransomware risks
- Ensure data availability from Microsoft 365 online cloud environments
- And more
Did you know maintaining backups is just one piece to maintaining business continuity? Learn about additional challenges that can arise due to a disruption and how to overcome them in our eBook.

